Metaverse in China
The term around the so-called metaverse always causes a stir with various news. What is the metaverse? What role does China play in it? What are the differences between a Western and a Chinese metaverse? Which companies and apps do you have to know about? This blog article provides a comprehensive introduction to the topic!

1. What is "Metaverse"?
Simply put, the metaverse connects the real and virtual worlds. The word is composed of “meta” and universe. By merging the two worlds, it should be possible to access real events within an artificial, virtual reality that can also be used in the physical world.
The metaverse is, so to speak, a digital 3D world that functions similarly to the real world. With a digital avatar, for example, it is possible to enter a virtual world – and basically perform all activities as in real life. Going for a walk, shopping, meeting up with friends, and so on.
The technology behind it
There is no such thing as “the one” metaverse. Rather, it is an idea and an ongoing technology whose original concept has been around for a long time and continues to evolve. The term was first popularized by Neal Stephenson in 1992 but is most often found in video games. Last but not least, Mark Zuckerberg, CEO of Facebook Inc, has brought the metaverse back into the spotlight. The company plans to focus more on developing a metaverse. As of October 28, 2021, the group has been renamed to Meta Platforms.
Virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) have played an important role in the development of the metaverse so far, as there are already everyday applications for both. Augmented reality allows users to see virtual objects in their natural environment. Examples include apps or tools that allow a user to virtually try on a new pair of glasses or place a new piece of furniture in a room. The game “Pokemon Go” has led to thousands of people chasing virtual Pokemon that appear on the streets – or rather on the screen. Virtual reality uses an artificial environment in which the user can interact with things using devices such as VR goggles. These are mainly used for video games in which players are immersed in a virtual world.
2. Metaverse in China
In addition to Zuckerberg’s Meta, the Metaverse trend is also leaving its mark in China. Just one day after Facebook changed its name to Meta, the Chinese search engine provider Baidu secured the “Metaapp” brand. Other tech giants also immediately jumped on the bandwagon, with Alibaba securing the “Ali Metaverse” brand, for example. In total, more than 400 companies have applied for trademarks on related terms in China.
According to a survey conducted by iiMedia Resarch in 2021, more than 85% of all Chinese netizens have strong, good or a basic understanding of the metaverse. Most expected applications are Game IP avatar, personal and community virtual space but also e-commerce related content. Only 10.6% are not willing to socialize in metaverse. Main concerns are the addiction to a virtual world as well as exacerbating real-life social phobia.
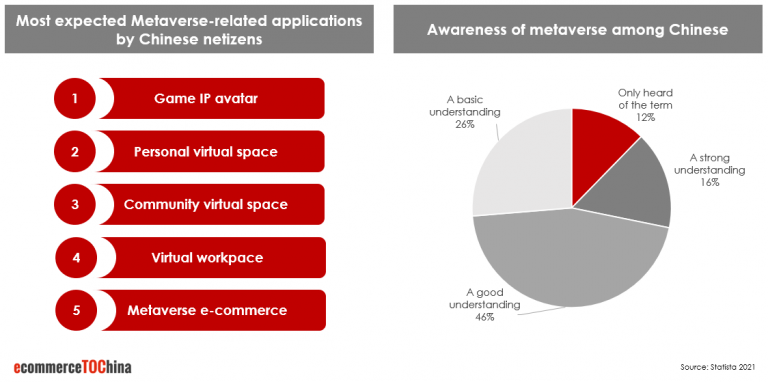
Here are some of the most important innovations and technological developments to metaverse-related terms in China:
Virtual Reality
In the field of VR and AR, China is already playing at the top. According to the American consulting firm IDC, the Chinese market for VR applications will grow by 68% in the next five years. Although most of the world’s VR goggles come from Oculus, which was bought by Facebook, Chinese rival companies are also quickly emerging. For example, Chinese company Pico was just acquired by TikTok parent company Bytedance in August 2020 and is also focused on VR devices.


Augmented Reality
The same is true for AR applications. The Chinese company NReal has been offering lightweight glasses since late 2021. These glasses can be used to display virtual content in front of the eye, as shown in the photo below. These glasses may be just the first step towards a device suitable for everyday use, because thanks to the latest technology, these devices require less and less weight, have more battery life, and so on. Basically, they are becoming as suitable for everyday use as a smartphone, which will continue to exist. And with that, a metaverse is also getting closer and closer.

VR glasses and AR glasses are not new inventions. Both ideas and devices have been around for several years but have not fully caught on. VR glasses were often used for video games or simulations but are not comfortable to wear in the long run or too expensive to purchase. This can be remedied by technological advances, for which China is also known. The 5G mobile standard will help make the VR experience more enjoyable and immersive in the future. The problem of so-called “motion sickness” that many users had when wearing VR glasses can at best be solved by this and thus opens up access to this technology to a broader mass. Important to know: According to the Global Times, China already has 757 million 5G users (as of February 2022). Furthermore, China already plans to commercialize 6G by 2030 which means even more opportunities.
Gaming
China has the largest gaming industry in the world with total revenue of around $46.6 billion in 2021. The largest video game publisher in the world is Chinese company Tencent, which also operates the super app WeChat. The total number of mobile game users in China is around 656 million. Needless to say, gaming is booming in China.
Nevertheless, the gaming industry is a thorn in the side of the Chinese government. As recently as August 2021, the industry was described as “spiritual opium”, as excessive computer gaming was harmful to children’s development. This hit Tencent particularly hard. Share prices fell by 10% in the meantime and Tencent took action: young people under 18 are now only allowed to play computer games for a maximum of one hour a day, and two on weekends.
Still, gaming plays an important role, especially for the metaverse. Increasingly, parallel worlds with their own currency are emerging in computer games, where consumers can spend in-game currency.
One outstanding example is Balenciaga, which has developed a new video game to showcase its fall 2021 fashion collection. It can be found on the company’s homepage and on the most popular Chinese social media. The player can navigate through a virtual world and discover Balenciaga fashion – like a virtual showroom.

Virtual Influencer
So-called “virtual influencers” are not only becoming increasingly popular around the globe but are also gaining considerable importance in terms of marketing in China.
Digital mascots, personalized avatars or even music bands are created by brands to promote products and create a unique experience.
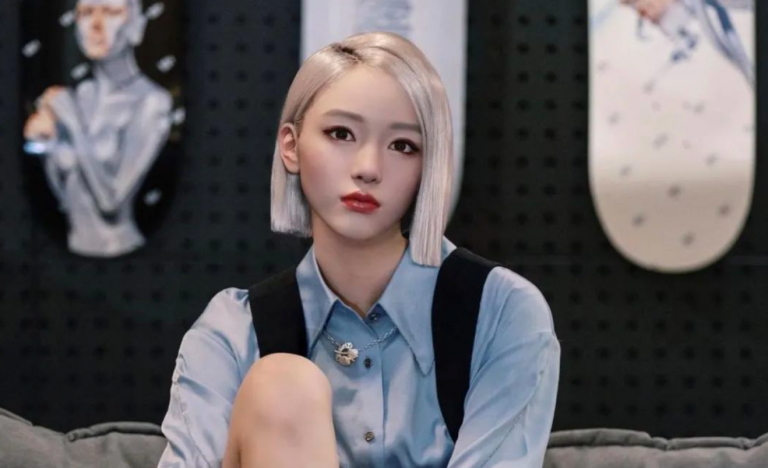

Compared to human influencers, virtual ones have no personal needs and do not make mistakes, but the development is quite expensive.
According to Bloomberg, the industry of these virtual KOLs reached $960 million in 2021, facing an audience of nearly 400 million people.
NFT
Another piece of the puzzle to create an own metaverse are NFT – non-fungible-tokens. These are purchasable digital objects like art or any kind of digital objects in e.g. video games. Through blockchain, NFTs are stored and thus remain unique and tamper-proof.
For the recent Singles’ Day on 11.11.21, Alibaba has released a “Metaverse Art Exhibition.” China’s first meta-human named AYAYI guided customers through the virtual world. The art exhibition features NFT artworks that can be purchased. Each artwork is unique as it has its own identification number and is fully protected for its owner. People can put on VR glasses and walk the exhibition digitally.

As with gambling and cryptocurrency, NFT is also subject to regulations and restrictions in China. Instead of objects for trading, they are merely digital collectibles in China, which in turn suggests a different benefit to customers. Therefore, they have to be marketed differently.
3. Where is China's Metaverse now?
XiRang
All the above examples are just parts of a metaverse. Baidu was the first Chinese company to unveil a real metaverse.
Xi Rang, the name of this metaverse platform means “land of hope” and is accessible via smartphone, computer or VR glasses. With a self-created avatar, the “Creator City” can be freely explored. Along the way, you can interact with other players and explore the city, nature, sights like Shaolin temples together or compete in competitive mini-games.
In an example video, it was shown that 100,000 users could participate in a meeting at the same time in a virtual conference hall. According to Baidu’s vice president Ma Jie, it may take up to six years before full launch.

Zheli
In February 2022, the social app Zheli (啫喱) caused a big stir in China. After just a few days, the app became the first since 2019 to temporarily replace super app WeChat in Chinese iOS app stores, with a record 435,000 downloads.
Zheli is a different kind of Metaverse, in which users can create a 3D digital avatar and interact with their friends. After the massive user rush, the app has been removed from the Appstore for the time being to further improve it for existing users and stabilize its performance. However, compared to traditional messenger services, Zheli lacks many typical features, such as photo sharing or emojis. Privacy concerns also caused controversy. This is just another example of how a metaverse seems to be met with great enthusiasm in China, but also brings many hurdles with it.
Mengke VR
The idea of the metaverse is not only found in social media apps, but also used for other activities. For example, a metaverse concept was developed for the Chinese Academy of Governance. The aim is to train cadres. It is a key training school for government officials and the Beijing company Mengke VR is one of the technology providers of the system. In a virtual environment, the trainees can experience a more effective party-building experience.
It combines educational and entertaining aspects. With technological equipment it allows its students to also visit historic places and exchange with others, while attending the actual classes.

Taobao Life
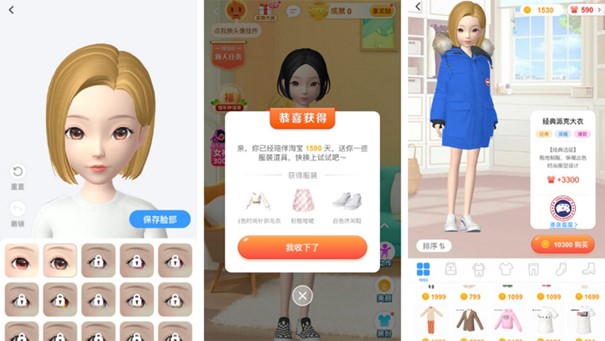
Taobao, the C2C e-commerce platform of Alibaba launched the application Taobao Life in 2019.
Taobao Life allows its users to create their own virtual avatars and enter a virtual shopping world where they can also buy real products. By purchasing goods on Taobao, you can also reward coins that you can spend in Taobao Life. Additionally, users can create their own home, decorate it and exchange with friends on the platform.
4. What’s next with Metaverse in China?
According to Morgan Stanley, the metaverse market could be worth $8 trillion in the future. Although the basic prerequisites for a metaverse are certainly given in China, the Chinese government has so far viewed this rather critically. Decentralized cryptocurrencies and NFTs are partly banned or partly strictly regulated. It can be assumed that China – as in many other areas – will develop its own metaverse, which is not directly comparable with the ideas of Mark Zuckerberg. While China has taken a global pioneering role in mobile payments, this remains to be seen in the metaverse sector. One clear difference, however, is that the companies faced little regulation at the beginning and were free to develop and experiment on the topic of mobile payment. This is not the case with the Chinese Metaverse. According to Deloitte, a mature integration phase of the metaverse in China can be expected as early as 2031. The use of a 6G network is inevitable, as is the high demand for computing power. Nevertheless, it seems just a matter of time when digital turns into virtual.

Discover the Future of Shopping with "Shopatainment – The Future of Shopping"
Our new book “Shopatainment – The Future of Shopping” explores how the innovative fusion of shopping and entertainment is revolutionizing the way we shop. Learn about the origins of this trend in China, the technologies and formats being used, and the opportunities and challenges it presents for the West.

Want to have a first free consultation session about how to do marketing in China? Contact us.
